Google Search Network Campaigns: Complete Guide 2022
How To Advertise On Google Search Network - Step-by-step Tutorial 2021-2022

Google Search Network can help you reach potential customers who may have difficulty finding your website on the web, including those that aren’t as actively looking for your product or service.
We’ll talk about search network campaigns, text ads on the search results page, how to optimize these ads, and troubleshooting tips and suggestions.
What is Google Search Network?
Google Search ads can appear on the Google Search Network and other networks, like the Google content network or Google shopping network. This article covers how to manage your campaign when you advertise on the Google Search Network.
In this article, you’ll find a complete guide to the world of Google Search advertising. You’ll learn everything there is to know about Google Search Ads, to become a PPC Hero.
Google Search Ads Guide Quick Navigation:
- Step 1. Google Ads Conversion Tracking
- Step 2. Campaign Objectives: Choose the most appropriate goal
- Step 3. Targeting and audience: Choose who you want to reach
- Step 4. Bidding and Budget: Determine a bid strategy based on your goals
- Step 5. Set Up The Ad Group, Enter Keywords
- Step 6. Create Google Search Ads
- Step 7. Add Negative Keywords To Your Campaign
- Step 8. Remarketing: Create Remarketing Lists for Search Ads (RLSA)
- Step 9. Optimize Your Google Search Network Campaign
- Step 10. Google Search Network Ads Best Practices
![]()
1. Google Ads Conversion Tracking For Search Campaigns
Conversion tracking involves generating an HTML code in the Conversion section of the Google Ads account that you insert into your landing page on your website immediately after your lead reaches the conversion event (i.e. “Thank you page”, “Order Confirmation” or “Thanks for Your Email”).
Check out the complete tutorial on how to set up Google Ads Conversion Tracking

2. Create Campaign And Choose Objectives: Choose the most appropriate to your goals
Create New Campaign
2.0. Navigate to Campaigns section ➜ + create NEW CAMPAIGN

2.1. Select the goal that would make this campaign successful to you
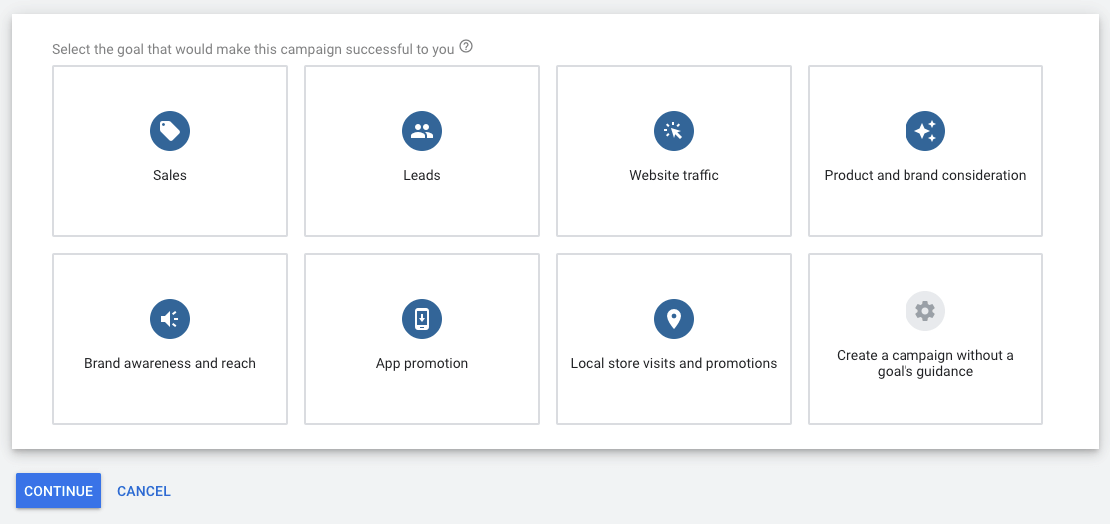
In order to run Google Search Ads choose one of the following campaign goals:
- Sales
- Leads
- Website traffic
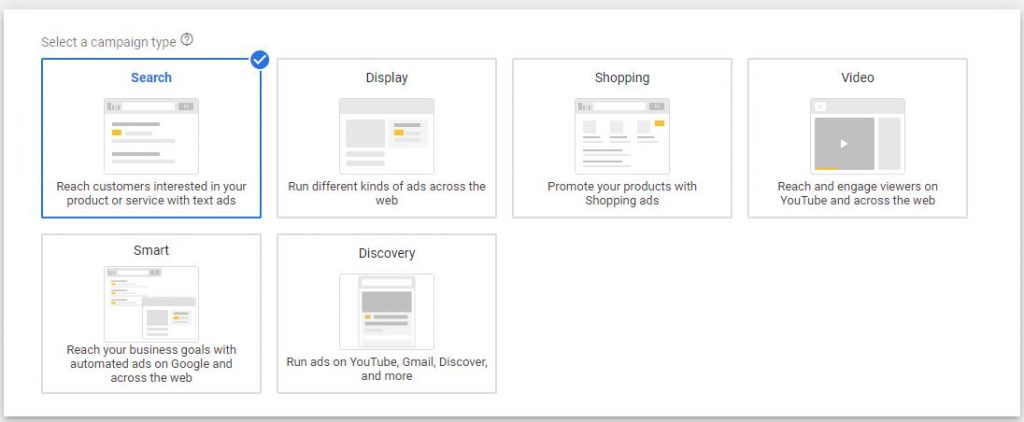
2.2. Select a campaign type ➜ Search
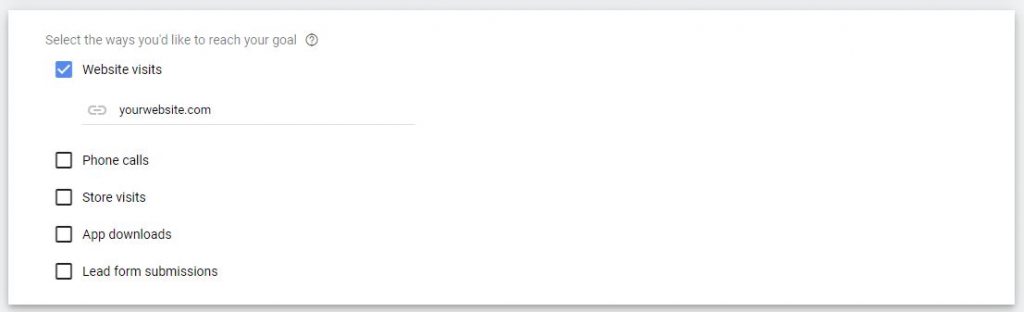
2.2. Select the way you’d like to reach your goal ➜ Website visits
2.2. Give your campaign a name ➜ Select/Deselect networks
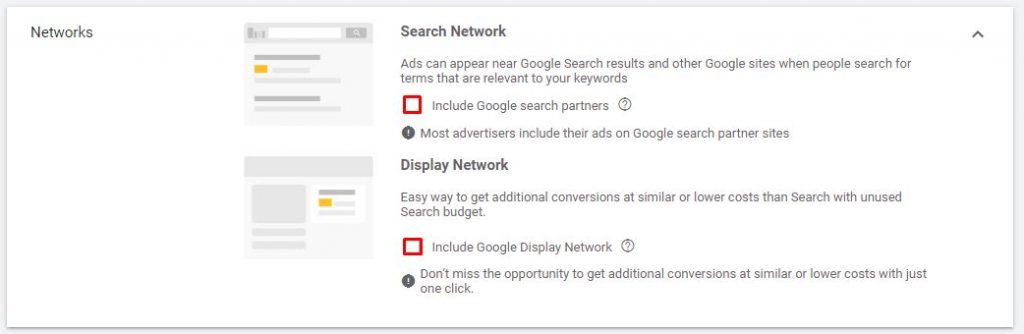
NOTE: I would suggest deselecting Google search partners sites and Display Network. This means that your ads will only run on Google Search Network.
The benefits of this are following:
- focus your budget in the right place
- knowing exactly where your ads are showing
- more control over click fraud

3. Targeting and audience: Choose who you want to reach
3.0. Enter your campaign name ➜ Choose the target location
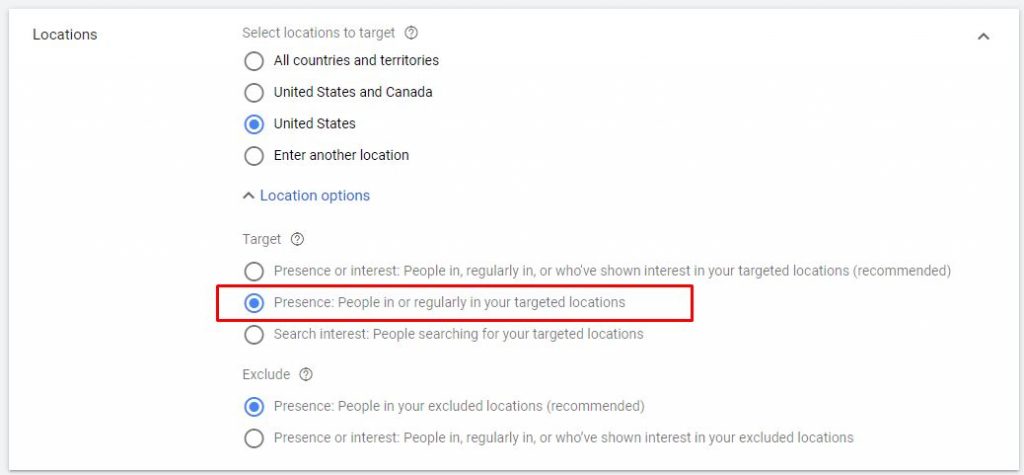
❗ Make sure to check the option: People in or regularly in your targeted locations. Otherwise, your ad will be shown to all people from the globe who showed interest in your targeted location.
3.1. Select the languages your customers speak
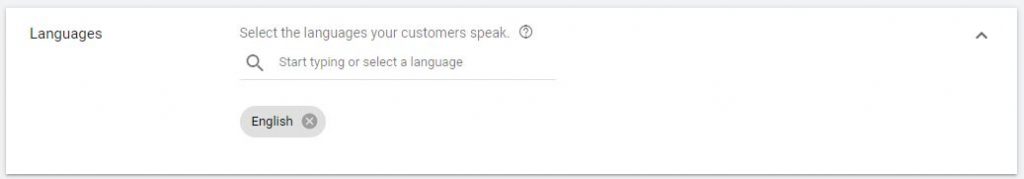
3.2. Audience
You can skip this section whether you don’t want to retarget users who previously visited your website. This is basically known as Remarketing Lists for Search Ads (RLSA).
Remarketing lists for search ads (RLSA) is a Google Ads feature that allows advertisers to tailor their search campaigns based on whether a user has previously visited their website (or app), and the pages that the user viewed.
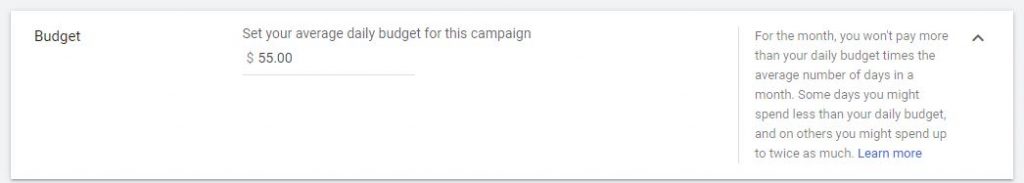
4. Budget and Bidding: Define how much you want to spend and how you want to spend it
4.0. Set your average daily budget for this campaign
4.1. In the bidding section select bid strategy directly ➜ Select Manual CPC
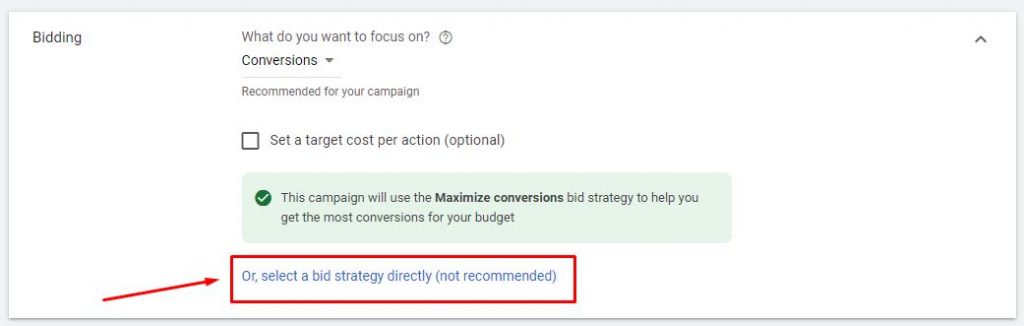
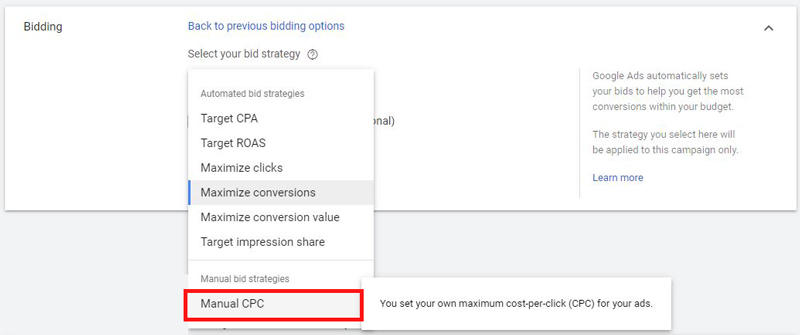
If you’re launching a brand new Google Search campaign I’d recommend starting with the Manual CPC bidding to have more control over your bids and spend.
After optimizations and sometimes of running you might switch your campaign bidding to Automated bid strategies as follows:
- Target CPA
- Target ROAS
- Maximize clicks
- Maximize conversions (be cautious with this type of bidding, cause it most likely overspends your budget)
- Maximize conversion value
- Target impression share
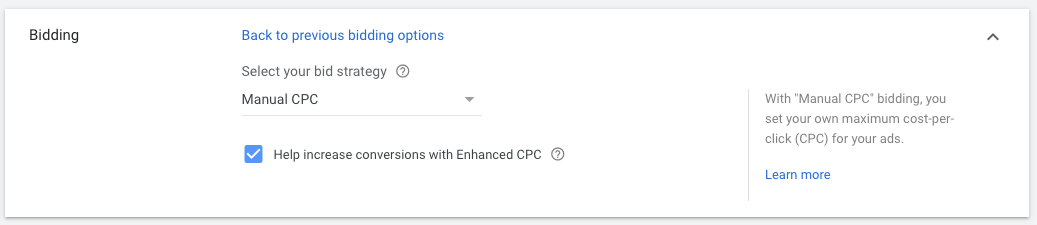
PRO TIP: A lower cost per click (CPC) isn’t always better.
Because Google Ads works in an auction system, the price fluctuates depending on how much advertisers are willing to bid.
When bids are higher it’s likely (not guaranteed) they can afford to bid higher because the ad is more likely to convert and turn into a sale – and therefore produce a good ROI.
4.2. Conversions ➜ Select which conversions are included in the “Conversions” column for this campaign
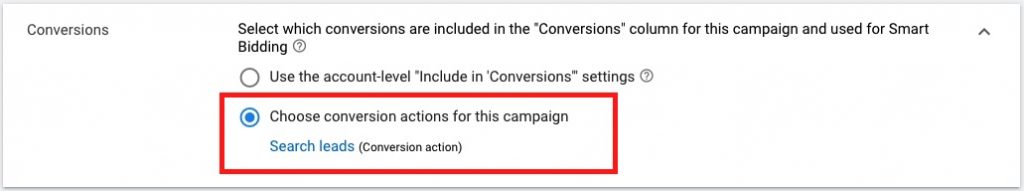
Select the earlier created conversion action
4.3. Ad rotation

4.4. Ad extensions
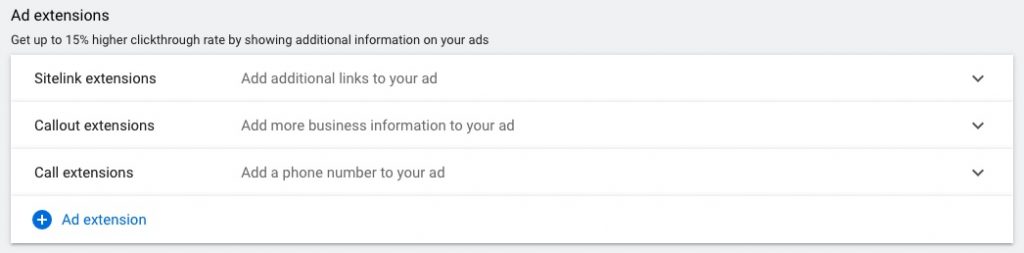
Get up to 15% higher clickthrough rate by showing additional information on your ads
For Google Search ads you can use the following extensions:
- Sitelink extension
- Callout extension
- Structured snippet extension
- Image extension. To use image extensions, make sure you have:
- A good history of policy compliance.
- A Google Ads account in an eligible vertical or sub-vertical. Sensitive verticals or sub-verticals—such as sexual content, alcohol, and gambling – aren’t eligible for image extensions.
- A Google Ads account that has been open for more than 90 days.
- A Google Ads account with active campaigns, and running Search campaigns so that there are active text ads.
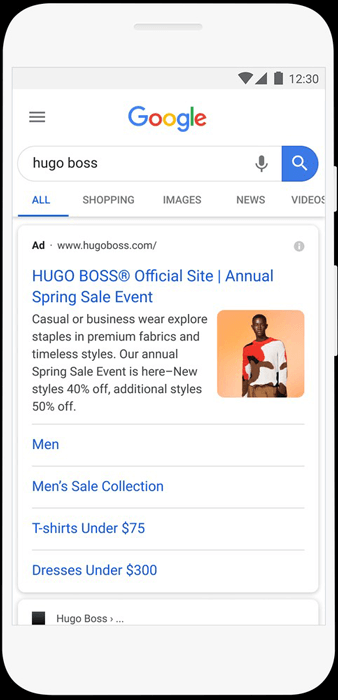
- Call extension
- Lead form extension
- Location extension
- Affiliate location extension
- Price extension
- App extension
- Promotion extension
NOTE: Some of the extensions will not be available from the beginning, i.e. Image extensions will become available after some spending, 90 days of activity, and good history of policy compliance

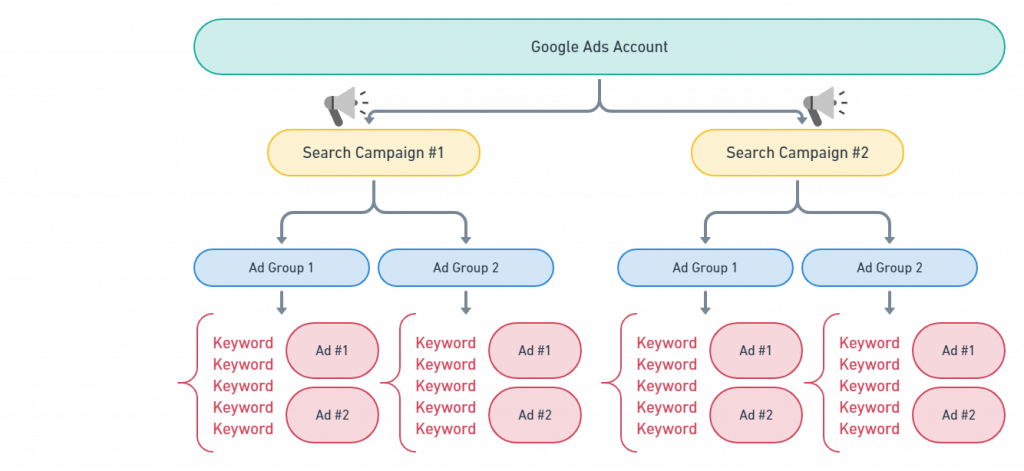
5. Set Up The Ad Group
Google Ads campaigns may include one or more ad groups. Ad groups are made up to help you group related keywords and write specific ads around a common keyword group.
Each ad group should be connected to the goal of the campaign.
Ad Group Structure
Keep these parameters in mind when structuring your account:
- Maximum of 7-10 ad groups per campaign
- Maximum of ~20 keywords per ad group
- Only 2-3 ads per ad group
Separate Ad Groups for Keywords
User intent is an important consideration when creating ad groups. Ideally, you should have separate ad groups for keywords with buying intent and keywords without buying intent.
TIP: You should avoid too many keywords in each ad group, as it will become bloated and unfocused.
5.0. Ad group name ➜ Give a name to your ad group

5.1. Default bid ➜ Set a default bid that reflects what a click is worth to you

KeyWords
5.2. Keywords ➜ Enter relevant keywords
Keywords are words or phrases that are used to match ads with the terms people are searching for.
Keyword Match Types
The keyword match types dictate how closely the keyword needs to match with the user’s search query in order for the ad to be considered for the auction.
So you could use broad match to serve your ad on a wider variety of user searches or you could use exact match to hone in on specific user searches.
Match types help control which searches can trigger your ads. Types of keywords matches:
- Broad match = keyword
- Phrase match = “keyword”
- Exact match = [keyword]
Broad match
The syntax for the broad match is to simply input the keyword. Below is an example of how a broad match will work:
Phrase match
The syntax for phrase match is to put quotes around your keyword, such as “tennis shoes”. Below is an example of how phrase match will work:
Exact match
The Exact match is designated with brackets, such as [red shoe]. Below is an example of how an exact match will work:
Matching the most relevant keyword to every search (Google newest update)
Previously, when you had multiple keywords that were eligible to match and none were identical to the search, your Ad Rank would determine which keyword served. Now, Google considers relevance signals in addition to Ad Rank when determining which keyword is selected.
Relevance is determined by looking at the meaning of the search term, the meaning of all the keywords in the ad group, and the landing pages within the ad group.
Here’s how it works:
| Keywords that are eligible | How keywords are selected |
| More than one broad match keyword | Only relevant broad match keywords from the most relevant ad groups will be considered. Ad Rank is then used to decide which keyword will be selected among this narrow set of broad match keywords with similar relevance. |
| One broad match keyword and one exact match/phrase match keyword | If you have exact match or phrase match keywords that are deemed more relevant than these broad match keywords, the exact or phrase match keyword will be selected. If you have exact match or phrase match keywords that are deemed similar or less relevant than these broad match keywords, there is still a chance the exact or phrase match keyword will be selected if it has a higher Ad Rank. |
| More than one exact match/phrase match keyword | If you have multiple exact and/or phrase match keywords eligible and no broad match keywords eligible, the keyword with the higher Ad Rank will be selected. |
For example, let’s say someone now searches for “quick sushi delivery near me”, and you have the phrase match keyword “fast sushi delivery” and the broad match keyword food delivery. In this instance, the phrase match keyword will be selected because it’s more relevant, even if it has a lower Ad Rank than the broad match keyword.
These rules ensure that the most relevant keyword will always be prioritized, so you can more easily use broad matches and still maintain control.
Best Keyword Grouping Structure
Based on the newest Google update, Google now recommends you group keywords into thematically consistent ad groups so your ads will serve from the ad group you expect them to.
For example, let’s say your business offers food delivery, and your most popular search categories are sushi and pizza delivery.
In this case, Google recommends three ad groups so you can tailor your creative and landing page:
- one for “sushi delivery”,
- another for “pizza delivery”,
- and a third for “food delivery”
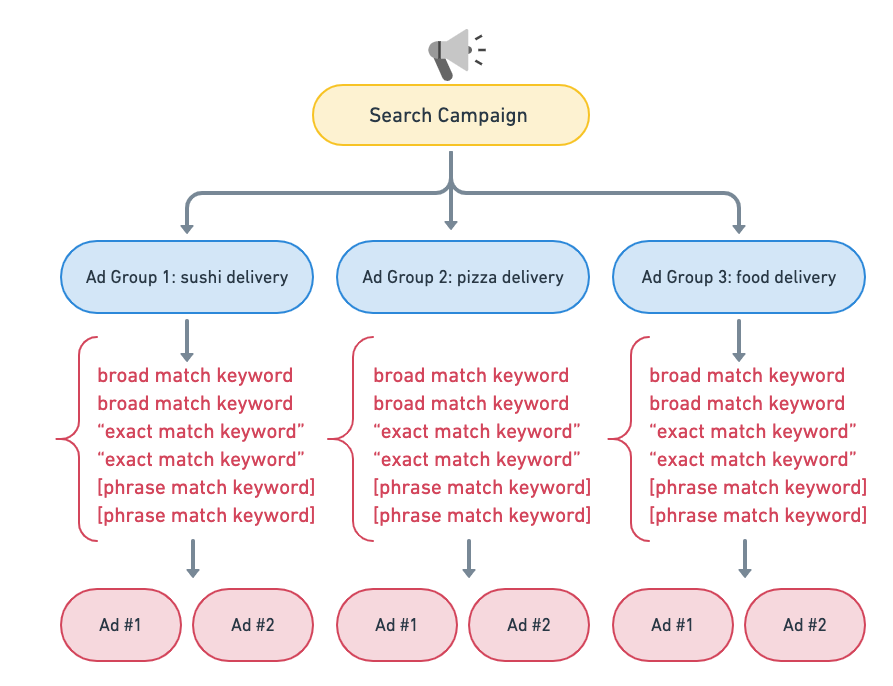
This structure gives you more control over which keyword matches a search query, particularly when using broad match keywords. It can also help reduce campaign optimization complexity: by prioritizing the most relevant keyword for every search, there’s no need to do extra work to control where traffic goes within your search campaign.
Check out Google Ads Keyword Research Guide for the best keywords research for your PPC campaigns.

6. Create Google Search Ads
Start with creating a Responsive search ad
With responsive search ads, you enter multiple headlines and descriptions and Google combines them into ads.
Why use Responsive Search Ads (RSA)?
- Responsive Search Ads were receiving 8 – 60 % more impressions than ETAs for most of the accounts I was managing.
- Working to reach a high ad strength for RSAs (higher than average) led to 74 – 400 % more conversions with 33 – 37% lower cost per acquisition (CPA).
- If the RSAs had an ad strength lower than average, the ads were less frequently triggered even though ETAs had higher priority and better KPIs.
Complete the fields all necessary information:
- Add the Final URL
- Display path

- Keyword insertion in Display path
- To use this feature in your ads, you insert a special piece of code into your ad text. For example, let’s say you’re running a campaign to advertise your candy store and you have an ad group that promotes your chocolate candy products. The snippet of code that you’ll insert in your ad text might look like the following: {KeyWord: Chocolate}. Doing this means that when a keyword can’t be inserted in your ad, we’ll insert Chocolate instead.
- You can also dynamically insert the user’s location in the Display path. To do so insert {LOCATION(City): United States}.
- Add up to 15 Headlines
- Add up to 4 Descriptions
 Click SAVE and publish your campaign for review
Click SAVE and publish your campaign for review
7. Add Negative Keywords To Your Campaign
After you’ve created your Google Search campaign, it is a good practice to add negative keywords. It’s important to identify and exclude from your campaign keywords-searchers – that wouldn’t deliver a return on your investment.
The main reason to exclude negative keywords from your campaign is to prevent your ads from showing up alongside search queries that are irrelevant or offensive.
For example, an advertiser of a high-ticket offer that would like to target affluent customers would want to exclude such terms as “cheap”, “free”, “no deposit” from the Search Network campaign by adding them to the negative list. This action will prevent your ads from appearing alongside those terms.
7.0. Navigate to Keywords section ➜ + Negative keywords ➜ Add negative keywords or create a new list
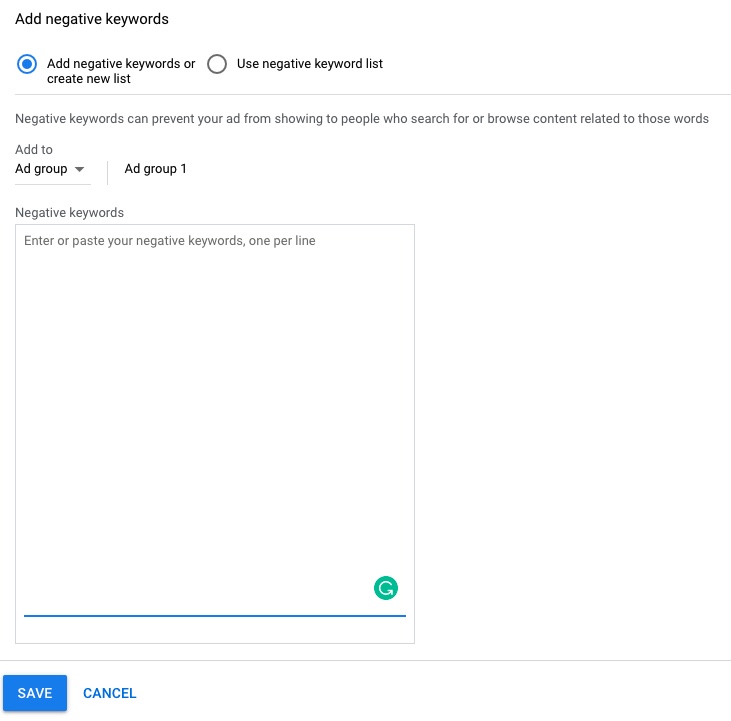
By avoiding paying for useless clicks, you save a lot of money by weeding out searchers who aren’t a fit for your business. You can also avoid bidding against yourself, cannibalizing impressions, and watering down your keyword-level data.

8. Create Remarketing Lists for Search Ads (RLSA)
Remarketing of your previous visitors is effective since prospects need to see your ad at least seven times before they become a customer.
Remarketing lists for search ads (RLSA) is a Google Ads feature that allows advertisers to tailor their search campaigns based on whether a user has previously visited their website (or app), and the pages that the user viewed.
RLSAs can be used in two ways:
- Making bid adjustments on your ad groups for users (remarketing lists) who are searching on Google using the keywords you are bidding on
- Set up search ad groups to only be triggered and show ads if a user is on your Remarketing list, and is searching with the keywords you are bidding on
How To Set Up Remarketing Lists for Search Ads
In order to create RLSAs, you’ll need to set up the Google Ads Remarketing Tag first.
1. Navigate to the Tools & Settings icon in the upper right corner of your account ➜ Click Shared Library

2. Click Audience Manager ➜ Audience sources
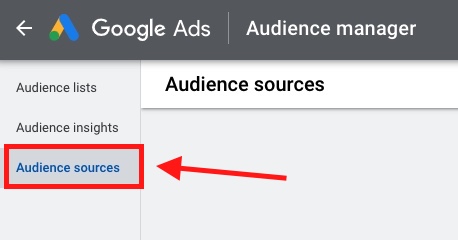
3. Under the Google Ads tag section click Set Up Tag

Select how you want to install the Google Ads tag:
- Add the tag to your website code
- Email the tag to your webmaster
- Install the tag using Google Tag Manager
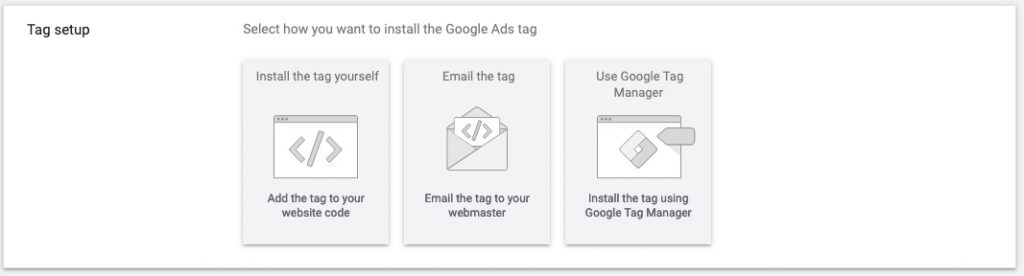
If you choose to Install the tag yourself, then copy the given tag and paste it in between the <head> </head> tags of every page of your website.

You only need to install the global site tag once per account, which can be used with both remarketing event snippets as well as conversion event snippets.
Setting up remarketing lists for RLSA
1. Go to the Shared Library ➜ Audiences Lists ➜ Remarketing
2. Click the plus icon + Remarketing button to create a remarketing list
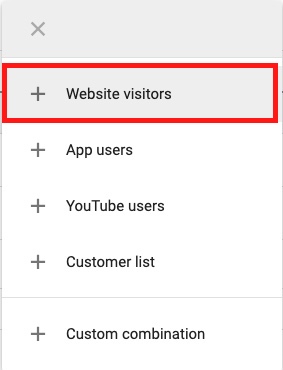
Select the type of visitors from which you’d like to create a segment (Remarketing list)

Remarketing Lists Best Practices
The most common practice of remarketing lists is to retarget people who visited check-out page but didn’t purchase your product (thus, haven’t reached your Thank You Page).
To do so:
- select Visitors of a page who did not visit another page
- in the Visited page section insert your product’s check-out page tag
- in the Unvisited page, section insert your thank-you page tag

Adding a remarketing list to a search campaign ad group
These instructions assume you’ve already created your search campaign and ad groups that you’d like to use with your remarketing lists.
- To add Remarketing List to your Google Search campaigns navigate to the Audiences section of your campaign and click plus icon + Add Audiences
- Click Browse ➜ Select Remarketing and similar audiences
- Go to Website visitors ➜ Choose your created list

9. Optimize Your Google Search Network Campaign
9.1. Improve your Google Ads Quality Score
If you’ve worked as a PPC/SEM Manager for some time then you probably have heard about the importance of improving your Quality Score.
It’s not only about getting high scores. You want those scores to impact positively on your bids, which means you’ll be able to buy more traffic for any given budget and the cost per conversion will decrease. You’re not only getting a medal. You’re winning the prize.
How to improve your Quality Score
Let’s see what Google says about how your Quality Score is calculated:
“Quality Score is calculated based on the combined performance of 3 components:
- Expected click-through rate (CTR): The likelihood that your ad will be clicked when shown.
- Ad relevance: How closely your ad matches the intent behind a user’s search.
- Landing page experience: How relevant and useful your landing page is to people who click your ad.”
But where do we shift our focus in order to improve the Quality Score of our keywords? Here are the three aspects you need to consider when optimizing your Quality Score (QS):
- Focus on keywords with QS ≤ 5 first.
- Label them so you can keep track of their performance.
- Check how closely tailored your keywords are to the ads and to the landing pages.
Learn more about Google Search Network Campaign Optimization

10. Google Ads Search Network Best Practices
10.1. Keep an eye on your search terms reports
Keywords ➜ Search terms report
This is a great way to find out what searchers are looking for when Google serves your ad.
If you see words in your search terms report that you know are not a good fit for your account, set them as negatives before you run the risk of showing for them again.
And wise verse, if you find queries that fit your campaign’s targets add them as keywords.
10.2. Check the Auction insights
Keywords ➜ Auction insights
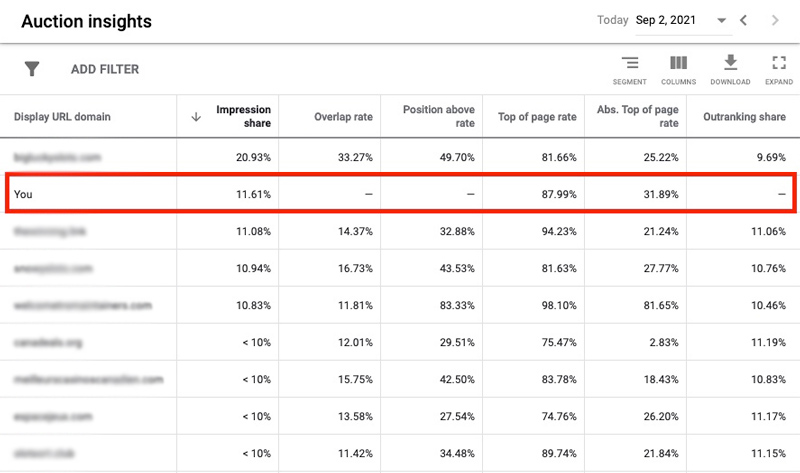
The auction insights report lets you compare your performance with other advertisers who are participating in the same auctions that you are.
This information can help you make strategic decisions about bidding and budgeting by showing you where you’re succeeding and where you may be missing opportunities for improved performance. Thus you might be able to adjust (increase or decrease) your bidding and budget accordingly.
The auction insights report is available for both Search Ads and Shopping campaigns.
10.3. Dynamic Text Replacement
Use Dynamic Text Replacement feature to increase Google Search campaign’s CTR and ROI
10.4. Remove duplicate keywords from your Search campaign
It might seem like you are getting traffic and even conversions from each or some of the duplicate keywords, so you might consider keeping them.
But in reality your keywords will be just competing against each other in addition to competition with your competitors.
The easiest and fastest way to remove duplicates is to use Google Editor. Here’s how:
- Select Tools from the top menu.
- Click on find duplicate keywords.
- Specify your criteria for duplicate keywords.
- Click on the button Find duplicate keywords.
- To decide which keywords to pause, download the relevant statistics for your campaign goals. You can find this
- feature on the top right corner of Google Editor next to the post button.
It’s also possible to remove duplicate keywords using Google Ads Web Interface.
To find duplicate keywords on the platform:
10.4.2. Navigate to the Keywords Tab ➜ Sort the keyword list by name or match type to find the duplicates alphabetically
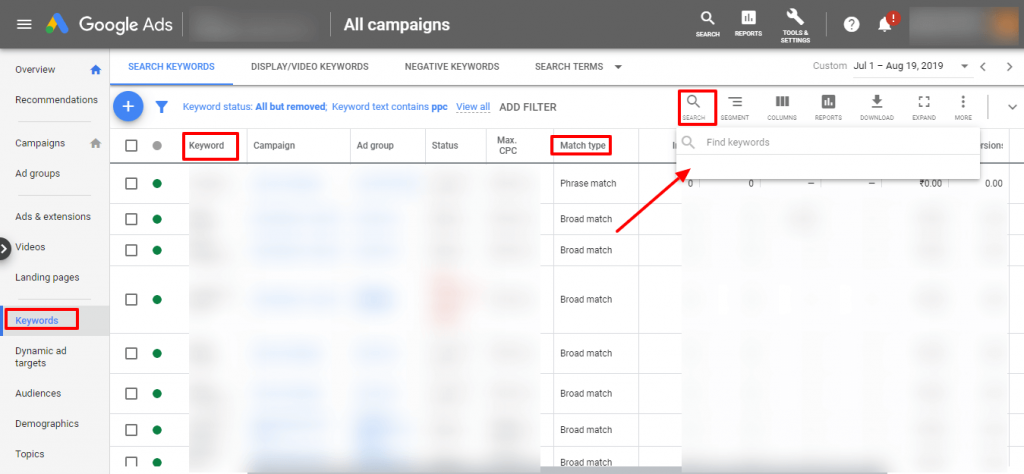
You can manually enter the keyword for which you wish to search the duplicates, in the search box that says “Find Keywords”.
P.S. I’d sure love to hear what you think about this post! Just drop a line in the comment section below and share your thoughts or questions.
Cheers 👋






