Facebook Ads Complete Guide 2023. How to Advertise on Facebook
Ultimate Guide to Facebook Ads Campaigns. Step-by-Step Tutorial on How to Advertise on Facebook

When it comes to online advertising, Facebook would be one of the first places you might think about.
Facebook is the largest social media network, with more than two billion monthly active users, and it continues to grow daily.
But with all of Facebook’s smart features and huge user base, it can spend all your budgets without any significant results for you.
In this complete guide, I’ll help you avoid all negative consequences of the Facebook advertising platform and to profit more consistently with the most powerful ads platform on the planet.

In this guide, you’ll learn exactly how to launch, track, optimize, and analyze your Facebook advertising campaigns, including:
- Step #1: Set up the Facebook pixel
- Step #2: Create a right campaign structure
- Step #3: Choose the Campaign Objective And Conversion Event
- Step #4: Choose the type of budget management: CBO or ABO
- Step #5: Choose the Bid Strategy
- Step #6: Audience Testing & Targeting
- Step #7: Choose the right placements
- Step #8: Choose the best type of Ads
- Step #9: Which types of Facebook ads to use
- Step #10: Best Messaging Strategies for Your Facebook Ads
- Step #11: Scaling
- Step #12: Retargeting
- #13: PRO Tips and Best Practices
Step #1: Facebook’s Pixel. Keep Track of Users on your website
![]()
The Facebook pixel is a piece of code you place on the backend of your website to track visitors to your site. The pixel allows you to run highly targeted campaigns, so it’s important to install it before running Facebook ads.
Each ad account gets one default pixel to use. The code is made up of two main parts: the pixel base code and the event code. The pixel base code tracks all of the traffic to your site. Event codes are additional pieces of code you can add under the default pixel code to specific pages of your website that allow you to track certain actions on those pages.
Install the base pixel code on your website and Facebook will begin tracking immediately.
Learn more about Facebook Pixel Set Up
Step #2: Create a right campaign structure

The advertising campaign that you create in Facebook Ads Manager has three levels (parts):
- campaign level
- ad set level
- individual ads creatives
This is called the campaign structure.
Knowing how the parts work together will help you run your ads the way you want to and get them to the right people.

Start at least 5 ad sets with different audiences for A/B testing
Step #3: Choose the Campaign Objective and Conversion Event
Facebook offers 11 marketing objectives based on your ad’s goals. Here’s how they align with business goals:

Optimize for the pixel event or objective goal you want to achieve.
If you optimize your campaign for conversions – this might be:
- Purchase
- Complete Registrations
- Lead
- View Content
- Search
- Subscribe
- Add to cart
- Add to wishlist
- Contact

Step #4: CBO or Ad Set Budgets? What’s Best?

CBO stands for Campaign Budget Optimization and is no longer just a best practice.
There are two ways to set your budgets in the land of Facebook Ads.
One is at the ad set level, allowing you to set a budget for each ad set within a campaign.
CBO, on the other hand, is a (relatively) new Facebook advertising feature that allows you to set a daily budget for an entire campaign rather than setting budgets for each ad set.
To dive deeper, CBO utilizes Facebook’s algorithm to distribute your budget across ad sets where they will most likely get conversions for the best price.
Instead of maintaining a constant spend per ad set, Facebook will pool the budget into the ad sets most likely to get results on any given day.
Source: www.fetchfunnel.com
So how do we go about testing with CBO?
Below is an easy print and reference cheat sheet followed by a step-by-step guide.
Let’s dive in!
If you’ve not been through the introduction to CBO, there are a few things you need to recap:
- CBO is a learning system different from ABO (Ad set budget optimization) – the decisions made on which audiences and ads focus on adapting during the day.
- Suppose you constantly use a single CBO for testing and scaling, pausing ad sets and ads as your testing cycles end. In that case, this causes issues with ML (machine learning) – the clever nerdy stuff that Facebook implements to help you achieve your goals.
- CBO gets better over time, with stability – meaning the fewer edits you make on ad sets and ads, the better the CBO learning algorithm becomes. Strength, on average, should be there within 5-10 days, but it highly depends on the factors I cover below.
- CBO does not entirely replace the need for ad and ad set-level optimization to pause/replace bad performance.
- However, CBO used right gives better stability and reduces the need for constant tweaking and analysis, freeing you up to focus more on marketing, offer creation, and your funnel.
- CBO gives faster results with qualified ad sets and ads – if they are pre-tested as ‘working’, you’ll get stability and strong results faster.
NOTE: Campaigns with smaller budgets (below $200 daily) with Ad Set Budget Optimization (ABO) provide better results faster and are more stable
Source: The Ultimate CBO Cookbook (for Facebook Ads)
Depending on how long it typically takes for someone to complete a valuable action (conversion) after clicking or viewing your ad, select your conversion window.
I would start with a 1-day click, meaning that Facebook will optimize ad delivery by using data from conversions within one day of someone interacting with your ad.


Step #5: Choose the Bid Strategy
In the fast-paced digital advertising landscape, businesses constantly seek ways to optimize their marketing efforts.
Facebook is a dominant force among the various platforms, providing a vast network of potential customers.
However, understanding its ad bid strategies is crucial to maximizing Facebook’s advertising potential.
Cost Cap Bidding (Formerly Cost per Result Goal)
One popular bid strategy offered by Facebook is Cost Cap Bidding. This approach ensures advertisers achieve their desired results (conversions, leads, purchases) at a maximum cost.
Businesses can control their spending by setting a cost cap while aiming for optimal campaign performance.
Facebook’s algorithm optimizes bids in real-time, distributing ads to audiences most likely contributing to the desired outcomes at or below the set cost.
This strategy best suits businesses with a specific target cost and wishing to maintain control over their campaign spending.

Bid Cap Bidding
As the name suggests, Bid Cap Bidding enables businesses to put a cap or maximum limit on their cost-per-click bids.
When using a bid cap, you determine the maximum amount that you are willing to spend per auction without exceeding it.
Suppose you offer a range of affordable items, like a set of graphic tees priced at $10 apiece. To make a profit, you require a minimum of $7 per sale. Therefore, you can only afford to spend up to $3 on each sale.
With Bid Cap, you can establish a maximum bid of $3 to guarantee that every conversion results in a profit.
This strategy is particularly useful for businesses with budget constraints or those aiming to stay within a specific bid range.
Advertisers can exercise control over a campaign’s cost by setting a bid cap while allowing Facebook’s algorithm to optimize performance.
Maximize the number of conversions (Formerly Lowest Cost) Bidding
For businesses seeking maximum outreach, lowest-cost bidding is a compelling strategy. This approach allows advertisers to reach the largest possible audience within their budget by automatically optimizing bids for the lowest cost per outcome.
Facebook’s algorithm considers various factors, including ad relevance and competition, to achieve the lowest possible cost for desired results.
This bid strategy is perfect for businesses looking to expand their brand reach and drive significant traffic to their website or landing page.
Step #6: Audience Testing & Targeting

The purpose of audience testing is to find the winning ones.
NOTE: it is common to make a minimum difference per ad set for accurate A/B testing, for instance, set 1-2 of the below options:
- Age:
- 25-35
- 35-45
- 45-55
- Gender:
- Male
- Female
- Interest:
- Meditation
- Physical exercise
- Running
- Yoga
- Demographics:
- Master’s degree
- New job
- New relationship
- Newly engaged (3 months)
- Behavior:
- Engaged Shoppers
- Frequent Travelers
- Facebook Payments users (30 days)
- Facebook Payments users (higher than average spend)
- Different Lookalikes (LAAs):
- LAA of users who visited the website in the past 30 days
- LAA of users who visited a specific page of our website
- LAA of leads
- LAA of purchases
NOTE: You may use excludes based on people who have engaged with/clicked on your ads to target pure, COLD audiences.

PRO TIP: When including interests, narrow your options to one interest per ad set. If you target more than one interest, you cannot attribute performance to a specific variable. Select one and only one, so you can pinpoint exactly why an ad does well.
Audience Exclusions
To create audience exclusions, go to Audience ➜ Create a Custom Audience


Broad audiences
NOTE: Broad audiences work!
A Broad audience is one without interests, behaviors, or LAAs. It may be split by age and/or gender but does not contain other narrowing options.
- Broad audiences can work better than interests, especially since FB introduced more data capture from their pixel to collect and understand the content and context of your website.
- Many advertisers still use narrow interest options to find winning audiences; however, greater success could be achieved with larger audiences and great ads.
- Aim to split broad audiences by a unique segment, where relevant. Examples:
- A broad audience targeting a specific age 18-30 in the US, split into an ad set for males and another for female
- A broad audience targeting the UK, where our market is women 25+, split into four ad sets of 25-34, 35-44, 45-54, and 55+ because our ads appeal to those segments in different ways
- A broad audience targeting the US, split by age and gender, into two separate CBOs: one is for Males and split by the same age group above, and the other is for Females with the same age splits where we deliver ads specifically by gender and age.
- If I have a single broad audience, say Canada 30+, and that’s my only target, with the same creative for them all with no further split, I’d duplicate the ad set 3-5 times so I can spread my bets wider and pause out any ad sets underperforming.
Minimum daily budget for each ad set
If your CBO campaign contains 5 ad sets with a minimum daily budget of $100 during the testing phase, set a MINIMUM budget for each ad set of at least $20 per ad set.
Use the calculation below for the MINIMUM budget:
(Total budget/number of ad sets) / 2
This is needed to spend fair across the ad sets in the test phase.
The screen below shows the ad set level, where to find ad set spend limits (expanded under the Optimization and Spending Controls).

500K+
Your estimated audience size should be 500K+
NOTE: As a rule of thumb, this is good for audience sizes of 500K upwards – below this, it can still work, but you will need to cycle more creatives more frequently as you’ll otherwise exhaust the audience too quickly.
Step #7: Placements

I would usually start with Mobile-only devices and Facebook News Feed placement. In another ad set, I would test Desktop devices only.

I prefer to test in the newsfeed before expanding to other placements (I prefer FB & IG in prospecting and All placements further down the funnel), but this will depend on your audience and how well your creative is set up to work with those placements.
I don’t include Audience Network or Messenger placements for testing because, in practice, these skew results, often quite badly in cases where Facebook may overspend in placements like Audience Network with very bad performance.
Step #8: Ad Creative

Create ads that trigger the only 3 things you need a user to do: stop, take notice, engage, and take action.
Don’t overcomplicate your ads.
Plan of creatives to test – ideally to test 3 angles (or pain points – a specific problem that prospective customers are experiencing), each with at least one ad copy and multiple visuals.
I would usually aim to have different ads with different formats:
- Image ads
- Video ads
- Carousel ads
- Collection ads
- Slideshow ads
- Stories
- Messenger ads

However, to start my testing, I’d use three ads in my ad set and those same ads in each ad set.
I aim to achieve my pixel goal: add to cart and form registration within around 2K-3K impressions.
If ads show bad performance, you have a few decisions to make:
- Is it the ad that’s bad? If you run three distinct ads or duplicate the same ad three times in an ad set, you can potentially tell if it’s the ad or the audience: if 1 or 2 ads work well and the third doesn’t – then it is likely the ad.
- If ALL ads equally performed badly in an ad set, it could be:
- That the audience is not a good one
- Or it could be that while the audience is good, Facebook delivers poor traffic. In this case, you may give the ads another go – often by duplicating and testing them again, which drops them into a different audience allocation with a clear history.
If the ad testing has successfully created new winning ads but you don’t need them in your main prospecting campaigns yet, copy them into a social proofing campaign (via Post ID sharing) – specifically created as a keep-warm Page Post Engagement (PPE) campaign, with a single broad audience.

Page Post Engagement (PPE) campaign creation
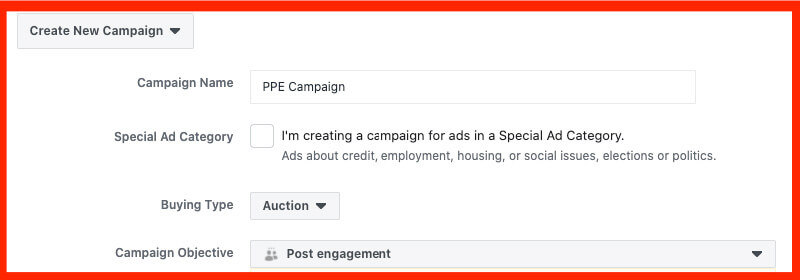
- Create a new PPE Campaign.
- Use the largest related audience you can, for example, a broad or large Interest or LAA – one ad set is only required because we’re only after social proof – expect some sales to trickle in too!
- Exclude site visitors and purchasers.
- The budget of $5 min. Multiplied by the number of ads, all active ads accumulating social proof/running.
- Copy ads from phase 1 or 2 testings in via their post ID (to share social proof)
- When you need them from scaling, copy them again via post ID into the scale campaigns. Leave the social proof campaign running!
NOTE:
Duplicate the winning ad set into a new CBO campaign to ensure the new CBO campaign contains only winning audiences so you can focus on finding new ads/creatives/angles that work.
Step #9: Understand which types of Facebook ads to use
To create the best Facebook ads, you need to keep the recommended character counts in mind. Anything beyond these text limits will be cut off.
You also need to understand which types of Facebook ads work with each ad campaign objective described above.
Image ads

- Headline: 40 characters
- Link description: 30 characters
- Body text: 125 characters
- Campaign objectives: All except video views
Video ads

- Headline: 40 characters
- Link description: 30 characters
- Body text: 125 characters
- Campaign objectives: All except catalog sales
Facebook Stories
- Text: No set character count. Aim to leave 250 pixels text-free at the top and bottom of the ad.
- Campaign objectives: All except engagement and store visits
Carousel ads
- Headline: 40 characters
- Link description: 20 characters
- Body text: 125 characters
- Campaign objectives: All except engagement and video views
Slideshow ads
- Headline: 25 characters
- Link description: 30 characters
- Body text: 125 characters
- Campaign objectives: All
Collection ads
- Headline: 40 characters
- Link description: n/a
- Body text: 125 characters
- Campaign objectives: Traffic, conversions, catalog sales, store traffic
Instant Experience ads
- Text: Blocks of text up to 500 words each
- Button text: 30 characters
- Campaign objectives: All except lead generation
Messenger Inbox ads
- Headline: 40 characters
- Link description: n/a
- Body text: 125 characters
- Campaign objectives: Traffic, app installs, conversions, catalog sales, messages
Step #10: Best Messaging Strategies for Your Facebook Ads
Creating effective Facebook ads that convert is not always easy, but you can use top messaging strategies to overcome it.
## Us vs. Them

One of the businesses biggest challenges when creating Facebook ads is standing out from the competition. With so many businesses advertising on Facebook, making your ad stand out can be difficult.
To overcome this pain point, focus on what sets your business apart from the competition and highlight those unique selling points in your ads. Use language that speaks directly to your target audience and appeals to their needs and pain points.
## Before & After

Another common Facebook ad pain point is showing your product or service’s before and after effects. While it can be tempting to show dramatic transformations, it’s important to be truthful and realistic in your ads.
To overcome this pain point, use customer testimonials and case studies to showcase the real results your product or service has achieved. Be sure to include specific details and statistics to back up your claims.
## FOMO

Fear of missing out (FOMO) is a powerful motivator, and it’s one of the biggest pain points businesses face when creating Facebook ads. If your ad doesn’t create a sense of urgency, your target audience may not feel compelled to take action.
To overcome this pain point, use time-limited offers and promotions to create a sense of urgency. Use language that emphasizes the limited time frame and encourages your target audience to take action now.
## X Reasons Why

Finally, businesses often struggle to communicate the benefits of their product or service in their Facebook ads. It’s not enough to list features; you must explain why those features matter and how they will benefit your target audience.
To overcome this pain point, use the “X reasons why” format to highlight the key benefits of your product or service. Use language that speaks directly to your target audience and explains how your product or service will solve their specific problems.
Step #11: Scaling

After you start seeing your campaign results, you may want to increase your ad spending so your profits will continue to grow. This is called scaling.

There are two most popular methods to scale your Facebook ads:
- Horizontal scaling techniques:
- duplicating the winning ad sets
- creating and adding new lookalike audiences based on Pixel results
- expanding the target geo
- Vertical scaling:
- Increasing the budgets
- Increase ad set budgets or CBO by 20-30% every 1-2 days if your campaign is performing consistently well for the last 3-4 days
- Increasing the budgets
NOTE:
- Scaling is not about how fast and how big to increase your budget but how well your campaign is primed and ready to pump the gas
- Facebook recommends increasing the budget by no more than 40% daily so it doesn’t impact the learning process. You may start with 20-30% daily scaling to play even safer.
Learn more about Facebook Ads Scaling Methods and Strategies.
Step #12: Retargeting

An advertising theory says that a consumer has to be exposed to an ad at least three times within a purchasing cycle (time between two consecutive purchases) to buy your product or service.
Retargeting is a method of finding previously engaged with your ad users to stimulate them to convert.
Does Retargeting Work?
You might be questioning whether this is just another marketing tactic that promises the world, only for you to struggle still to prove ROI once the campaign ends.
The truth is: Facebook retargeting does work, and the statistics prove it:
- Website visitors who are retargeted with display ads are more likely to convert by 70%
- The click-through rate (CTR) of a retargeted ad is 10x higher than the CTR of a typical display ad
- 44% of consumers say that they would likely become repeat buyers after a personalized shopping experience with a particular company
When we’re talking about Retargeting in the context of a profitable Facebook ad campaign, we mean first of a sales funnel with several levels from top to bottom.

When to set up a retargeting campaign?
- For the warmed audience:
- The user clicked on the ad and visited your landing page but didn’t convert
- People who have watched 50-75% of your video
- Viewed or added to cart but not purchased
- For existing customers
Great Retargeting Audiences
- Facebook engagement past 30 days
- Instagram engagement
- Email list
- Past purchases
- Website traffic past 180 days
How to set up a retargeting campaign?

A retargeting campaign starts with audience creation
A source for your audience might be:
- Email list of existing customers, which you shall load to the Facebook Customer list;
- Pixel-based events:
- Specific page visits;
- Specific CTA-buttons clicks (View Content);
- Signing up (Complete registration);
- Purchase
To create your retargeting audience for specific page visits:
1. Go to Audience ➜ Create a Custom Audience

2. Create a Custom Website Audience
- Choose the right Pixel ➜ Choose the option: People who visited specific web pages
- Indicate the specific URL of your Offer Page ➜ Name your audience


3. Create a custom website audience
- Choose the right Pixel ➜ Choose the option: People who visited specific web pages
- Indicate a specific URL of your Thank you page after the purchase has been made
- Name your audience

3. Create your retargeting campaign
- INCLUDE Offer Page Visits Custom Audience ➜ EXCLUDE Thank you page visits

In this scenario, you’ll reach people who have visited your offer page in the past seven days but didn’t purchase your product or service.
#12: PRO Tips and Best Practices
Tip #1: Use Facebook’s Automated Rules
Facebook Automated Rules allow you to create automated rules in Ads Manager, which will automatically check your campaigns, ad sets, and ads and then update or notify you of any changes.
Automated rules can help you manage multiple ads running at the same time. Think about the items you frequently check up on and your subsequent actions in Ads Manager. Facebook Automated Rules are designed to do these actions for you.
How to set automated rules?
Select the ad sets of your ad campaign ➜ Click on Rules ➜ Create a new rule.
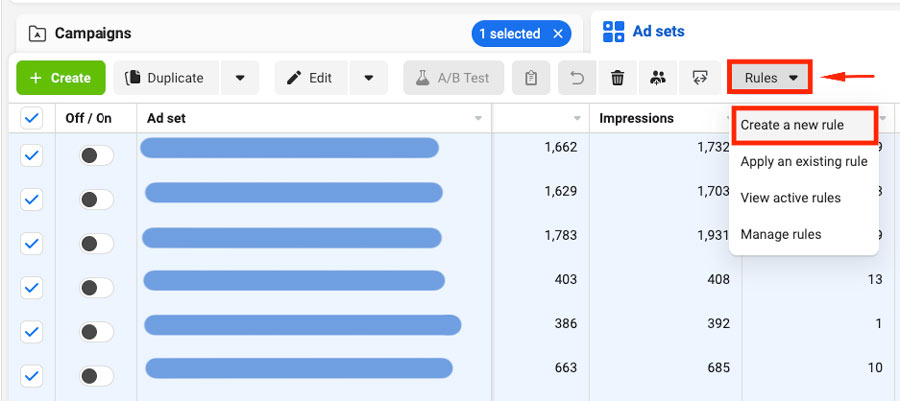
OFF RULE
Spend > CPA (or 1.1-1.5 x CPA — you choose)
Events < 1
Time range: Today

Purpose: if the day started poorly, better not to spend a lot of money on this ad set. If lifetime performance suits this ad set, we will switch it back later.
Learn more about Facebook’s automated rules.
P.S. I’d sure love to hear what you think about this post! Drop a line in the comment section below and share your thoughts or questions.
Cheers





